By now we all know header bidding has become a major focus in digital advertising. In the space of two years, header bidding has gone from virtually unknown to an industry standard, with nearly 70% of publishers using header bidding.
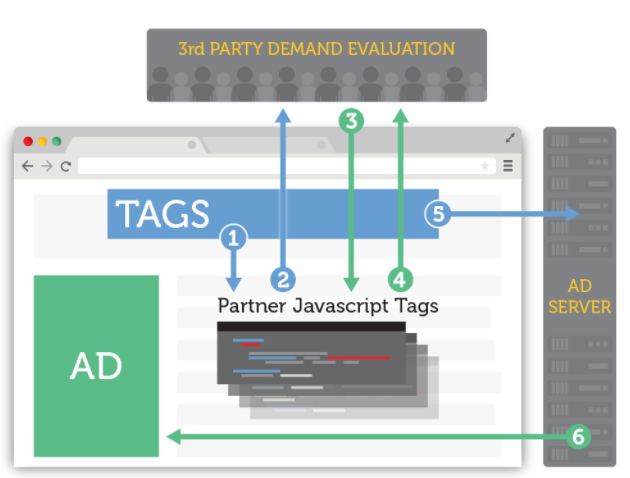
Up until now, publishers have mainly used browser-side header bidding. With browser-side header bidding, advertisers bid on the inventory inside the header of the publisher's web page.
The Challenge with Browser-side Header Bidding
In the space of two years, header bidding has gone from a virtual unknown to an industry standard. As previously mentioned, nearly 70% of digital publishers are using header bidding. However, most publishers have utilized browser-side header bidding solutions, which can potentially cause ad-load and page-load latency.
The biggest challenge here is that it can slow down the overall page load because you have a container directly on the page, the more partners you add, the slower your header bidding solution becomes overall. This means that the more advertisers you have competing in your on-page header auction, the slower the ads load which can lead to overall slow-loading pages and a bad user experience.
Even more, each ad partner bidding on the inventory has a different response speed, so your auction can sometimes work only as fast as your slowest bidder.
The Bottom Line?
With browser-side header bidding, publishers can be limited. They are incentivized to use fewer partners to prevent latency, which can be detrimental to ad performance. This type of header bidding is also dependent upon the speed of their header bidding partners. Furthermore, all of this is weighed against all other code functioning on their web page.
How Does Server-side Header Bidding Work?
Publishers now have another option: server-side header bidding.
Server-to-server header bidding allows the auction operations to occur outside of the publisher's site browser. Rather than having multiple calls coming and going from the web page, the auction is held after one call is sent to an external server.
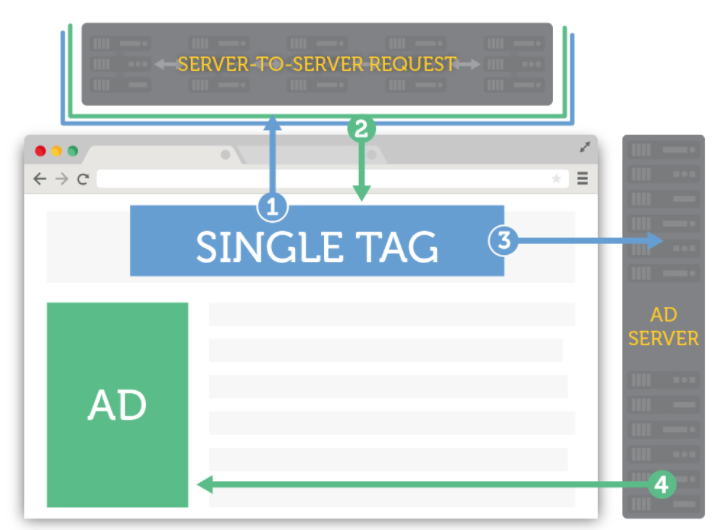
How does it work?
Advertisers bid on inventory ahead of the ad server within an externally hosted auction. Then, that ad calls inventory via a consolidated call process to the page. The overall process is much easier, resulting in reduced page latency.
Who hosts the header bidding server solution?
With server-to-server header bidding, the publisher chooses a server-side bidding technology partner to implement and host the solution. A few SSPs and Exchanges are working on these solutions already like Sovrn, Index, and Google. Sovrn is beta-testing its server-side header bidding solution. Google is expanding its traditional Ad Exchange only option for Dynamic Allocation with its beta Exchange Bidding solution.
If you have any questions about server-to-server header bidding, contact Sovrn Support.
